Identifying Chinese Vulnerabilities for Strategic Leveraging By Maj Gen AK Chaturvedi, AVSM, VSM (Retd)
![]()
Introduction
China is an emerging superpower, which has a vision to become the sole superpower of the World by 2049. Current Regime in Mainland China started as a communist regime in 1949 after defeating the forces of Republic of China and named it People’s Republic of China (PRC), in the process it pushed the Republican Govt headed by Chiang Kai Shek of Kuomintang to Taiwan. However, after becoming nuclear power in 1964 and having replaced Republic of China (Taiwan) as a UN Security Council member in 1971, the world started looking at PRC differently. In 1972 the then US President Ricard Nixon visited China and that heralded a new era in the Sino-US relations. Both had their respective interests; PRC was looking for getting identified as the sole representative of the Chinese people and US wanted to use PRC as a hedge against the then Soviet Union during the ongoing ‘Cold War’ between the Western powers (so called the ‘Free World’) and Communist forces led by the erstwhile Soviet Union. Chinese economy started opening up with the change in its leadership in late Seventies (After Mao Zedong’s death in 1976, Deng Shao Ping became the Paramount leader of China). The decade of Eighties saw the decline of Soviet Union which finally imploded in Dec 1991 and during this period PRC continued to grow economically. With Xi Jinping assuming the presidency of PRC in 2013, the world started seeing a more muscular China. Even US started feeling threatened with the rise of its former collaborator turning into a competitor. A Trade war commenced between US and China in 2018, when US imposed a rising tariff on certain imported goods from China and China retaliated by raising duties on imported US product. Chinese arrogance to deal with its neighbours, especially India, has created an environment where they feel that they need to come together to deal with China, resulting into formation of organisations like QUAD, AUKUS etc. The onset of Pandemic in 2020, though impacted the entire world, but China was one of the worst hit country and has yet to fully recover from the ill effects of the Pandemic.
Dream of China to reach the Numero uno position by 2049 is increasingly becoming a distant dream.
I have attempted in this paper to analyze some of those vulnerabilities which may impact China’s march to become the sole superpower of the World.
Issues-
Geographical Constraints– China’s problems are uneven water distribution between North and south, excessive concentration of wealth and wealth making resources in coastal areas whereas western China is not so well developed.

Map-1: Geographical Spread of China
- West and Southwest of China is inhospitable because of Gobi Desert and Taklamakan Desert. Xin Jiang (Erstwhile East Turkestan) which China occupied in 1876 during Qing dynasty period is located is located in this part of China. Uyghur Muslim population of Xin Jiang is quite restive due to human rights violations there and as a consequence a Jihadi organisation namely, ‘East Turkestan Islamic Movement’ is becoming active.
- Thereafter is Himalayan Range which hems China’s reach to Southwest. Here Tibet which China occupied in 1959 is not fully in control of China, despite a massive change in demography due to Han Chinese settlement of about 12.2%. China desperately needs Tibet because of its water resources and its mineral wealth.
- In the East, East China Sea, and South China Sea again hem China due to disputes with Japan and Taiwan. With Japan it concerns the different application of the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea-1982 (UNCLOS). Which has resulted into dispute about Chungxiao gas field. There is also a dispute between China and Japan over the ownership of Senkaku (Chinese call it Diaoyu) Islands.
- In SCS the dispute is wrt ownership of Spratly Islands between Brunei, China, Malaysia, the Philippines, Taiwan, and Vietnam. Further Approach to SCS is through Malacca Straight (70 % of petroleum and LNG heading for China and 60% of global maritime trade passes through Malacca straight) and which by their own admission is a dilemma (Word ‘Malacca Dilemma’ was coined by former President of China Hu Jintao) and despite best of efforts they have not been able to find a lasting and safe solution to it. Their effort to build Kra of Isthmus in Thailand and use Gwadar port in Balochistan of Pakistan have been non- starters. Similarly, Lombok and Sunda Straits in Indonesia are also not being found useful.
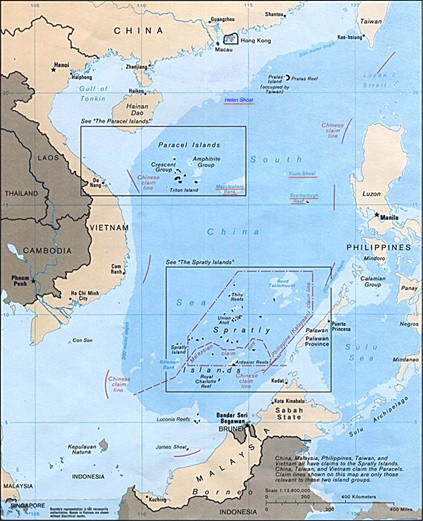
Map-2: islands of South China Sea
- Issue of Hong Kong Special Administrative Region which joined China with certain conditions known as ‘One Country Two Systems’ in 1997, remains alive, because in just two decades China has gone back on its promise and that is leaving people of Hong Kong feeling betrayed.
- In North, China borders Siberian Region of Russian Federation. Although China resolved Boundary dispute with Russia in 2003 but in recent times again China has started claiming Vladivostok in Russia. Inner Mongolia Autonomous region is In North China which became part of China only in 1947, after the WW-II, though has majority population of Han Chinese (78.7%) but the largest minority is Mongols (17.7%).
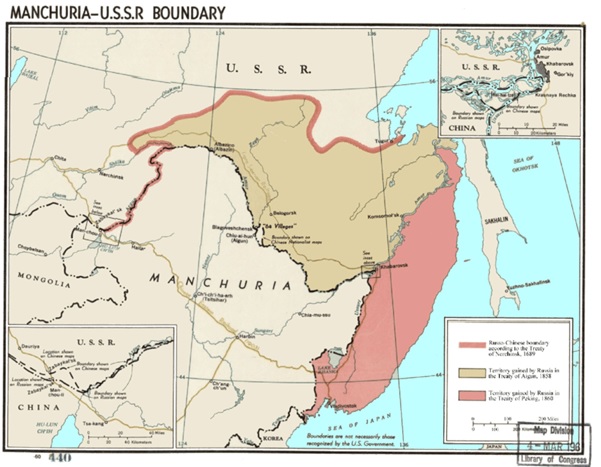
Map-3: Boundary between Russia and China
Impact of Climate Change– It has resulted into temp rise of 0.24 o C / decade which is higher than world average. China has become the largest emitter of CO2 . Sea level rise has been 3.5 mm/ year since 1980 as compared to 3.2 mm of the world average. One meter of rise would inundate 92000 sq km resulting into displacement of 67 million people. Almost 18 % of Chinese population and industry are in coastal areas, who will be severely impacted. Rise in temp will have adverse impact on health care and especially incidence of Malaria will increase. As per sixth assessment report of IPCS China will be impacted maximum due to climate change. Glaciers of Tibet will melt faster as Tibetan Plateau will see rise in temperature by four times. Recent flooding in Yangtze is a direct outcome of such a phenomenon, It will result into floods and impact water availability during lean period. This will result into internal displacement of 33 million people and 22 millions of livestock. Forest cover is likely to get reduced by 8% with attended problem. Rise in temp will facilitate rise in crop pests by four times and if not checked, will reach 243 % by 2100. Not only China but the food security of many of those countries who depend on China for import of food grains will be badly impacted.
Economic Dependencies– Some of the important issues are as follows:-
- Slowing growth– from a double-digit growth over last three decades, it has come down and the projected growth for the Fiscal 2024 is 4.5%. One of the major causes for the same is diminishing returns on investment in infrastructure. Investment in Airport and high-speed rail network is no longer remunerative.
- Mounting debt– to sustain high growth rates China had heavily relied on debt financed investments. In recent years debt has surged to over 280% of the GDP. It will impact financial stability. Although, most of the rating agencies have still kept investment grade as stable but Moody’s have put China on downgrade warning.
- FITCH has said that slowing down of China will impact the World, as China accounts for 40 % of global growth. Big exporters to China have started feeling the pinch has Chinese import has reduced by 9%.
- BRI projects which are spread over 150 countries and where China has invested over $ one trillion in last 10 years are likely to suffer if domestic economic problem continues.
- US trade restrictions have contributed to a 25% reduction in export to US.
- Reduced domestic consumption, shrinking workforce, and rising cost of production is impacting MNCs and flight of capital has started. One in 10 companies in the European Chamber survey said they have shifted investments out of China. Another 1 in 5 are delaying or considering shifting investments. In aviation and aerospace, 1 in 5 companies plan no future investment in China.
Internal Challenges– China has many problems especially post Wuhan based Covid -19 Pandemic. Some of these are as follows:-
- Shifting demography– ageing problem of population which is resulting into shrinking of work force and increase in the pension bill, increase expenditure of state on health care and public finance.
- Gender Imbalance– The one Child policy from 1979 to 2016 (and finally in 2021 permitting three children), had and still having repercussion for societal stability.
- Environmental Concern– rapid industrialization has resulted into air and water pollution and soil degradation. According to the Chinese Ministry of Health, industrial pollution has made cancer China’s leading cause of death. Every year, ambient air pollution alone kills hundreds of thousands of citizens. Today, 500 million people in China are without safe and clean drinking water.
- Food problem- Limited agricultural produce is not enough to feed the burgeoning population. China is already biggest importer of Agri products including meat, diary, soyabean and corn, though she is self-sufficient in staples.
- Mass unrest- post COVID-19 restrictions have resulted in a spike in the unrest which were in the range of 90000 earlier. As per Sophie Richardson China Director at Human rights’ watch, people across China are taking extraordinary risks to publicly demonstrate for their human rights.
- Unemployment- current rate is 4.9%, which though is lower than the world average (5.8%) but is still quite high.
- Regional Imbalance- the Rural and urban divide is widening. Dis[parity in 1978 was 2.56:1 had risen to 3.33:1 in 2009 which has further gone up. It has also resulted into income disparity also because it is 17175 yuan to 5153 yuan. Gini’s coefficient which is a measure of disparity has risen to 0.42, whereas anything above 0.4 is socially destabilizing.
- Simmering Dissension amongst the regions believed to be Occupied by China at Different Points in Time- Following map is quite explanatory on the subject.
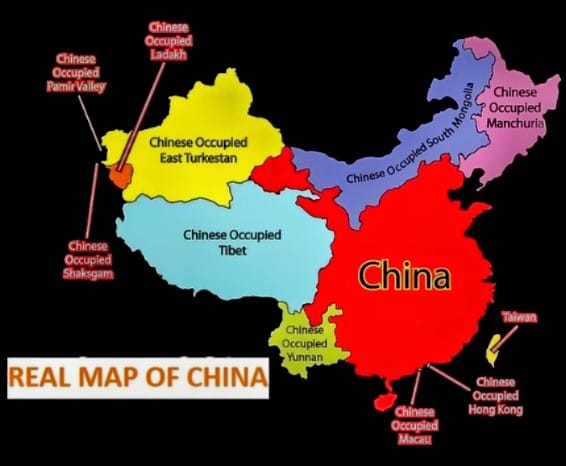
Map-4: Expansion of China over a period of Time
Diplomatic Isolation– With the current dispensation becoming more ambitious about its role in global governance diplomatic challenges are rising. Some of the challenges are as follows:-
- Worsening relations with the neighbours.
- Increasing rivalry with US.
- Improved relationship with Russia and Iran is pushing China in a corner.
- Reconciliation of Taiwan with Mainland is becoming doubtful due to US concerns in western pacific.
- Japan is shedding its pacifism and the latest defence budget for 2024 is $52.67 billion, which is 2% of her GDP which earlier was 1%.
- State of tension along LAC with India continues and besides US who is totally hostile to Chinese designs even Russia is not with China on Chinese adventurism on LAC.
- Tibet and Xin Jiang are both restive. US with out saying in so many words is working against their stated ‘One China’ policy. Ageing of 14th Dalai Lama and Chinese insistence to name his successor is making situation quite volatile. Xin Jiang is simmering with Islamic terrorism due to human rights’ violation there.
- Italy having decided to quite BRI has foreclosed option of China to get a foothold in Europe. Simultaneously newly proposed IMEEC is further likely to damage the prospect of BRI.
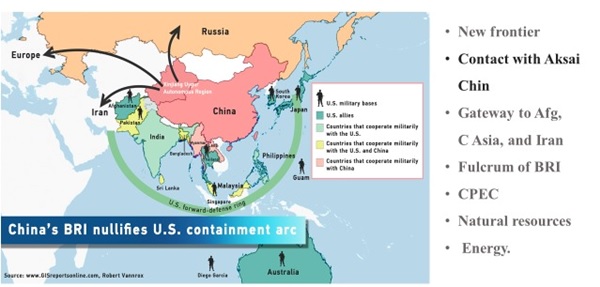
Map-5: Belt and Road Initiative of China
- Recent visit of Gen Asim Munir, COAS of Pakistan to US has potential to create a wedge between China and Pakistan.
- Iran–China 25-year Cooperation Program of $400 billion signed in 2021 appears to have become a non-starter.
- African Union becoming a member of G-20, at the behest of India, is further reducing the influence of China in Africa.
Conclusion
China, though a $17.70 trillion economy and with a FOREX reserve of over $3.12 trillion, is going through a bad time. However, her failure will impact the world substantially. However, her arrogance resulting into coercive diplomacy is not making matters easy for her. There is a need for a gradual weaning away of the manufacturing by western powers (especially USA) and Japan , from China. Further, the threats on account of climate change are major threat to her growth in years ahead. On the whole China is presently having a tough time in the current geopolitical and geoeconomics landscape and probably they need to go back to drawing board to work out a new strategy to deal with the emerging ‘World Order’.




